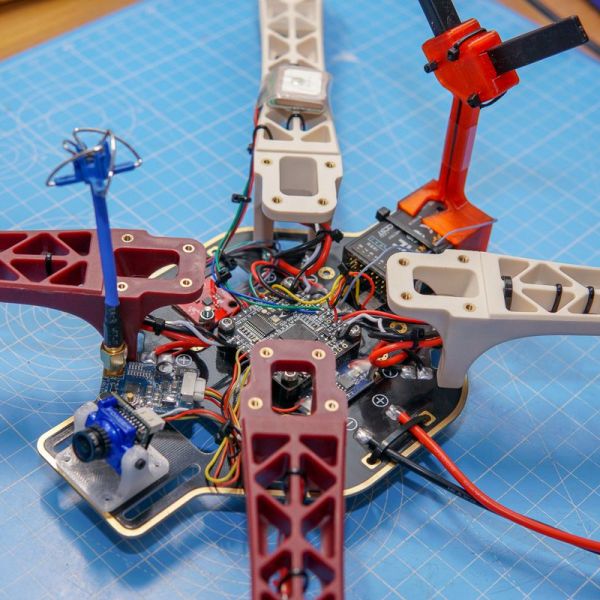
DJI F450 LTE Drone. It’s a cellular-connected quadcopter I built using a DJI F450 frame, LilyGO ESP32 board, and integrated 4G/LTE modem.
It’s designed for beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) operations with internet-based control instead of traditional RC links.
What It Can Do The F450 LTE Drone includes the following capabilities:
- Cellular Telemetry: Full MAVLink communication over 4G/5G networks
- Long Range Control: Operates anywhere with cellular coverage
- GPS Navigation: Autonomous waypoint missions and return-to-launch
- Live Video Streaming: Real-time camera feed over LTE connection
- Fail-Safe Systems: Multiple backup systems for safe operations
- Ground Station Integration: Works with QGroundControl and Mission Planner
What You Need To build this project, I used:
- DJI F450 Frame + Motors & ESCs
- Pixhawk Flight Controller + GPS Module
- LilyGO T-A7670G (ESP32-S3 + 4G Modem)
- 4G/LTE Antennas + SIM Card
- 3S/4S LiPo Battery
- RC Receiver (for fail-safe)
- Various cables and mounting hardware
How It Works
- Build the Hardware: Mount all components on F450 frame with proper power distribution
- Upload Firmware: ArduPilot on Pixhawk, custom MAVLink bridge code on LilyGO
- Configure Network: Set up cellular APN, VPN tunnel, and ground station connection
- Calibrate Systems: IMU, compass, ESCs, and fail-safe parameters
- Test Flight:
- Ground Tests: Verify all systems and connections
- Short Range: Test with visual contact first
- Long Range: Gradual range extension with cellular link
Performance Achieved
- Range: Limited only by cellular tower coverage
- Latency: 50-200ms typical (network dependent)
- Flight Time: 15-25 minutes depending on payload
- Control: Full autonomous mission capability
- Streaming: 720p video at 1-2 Mbps
Key Advantages ✅ Cost Effective: LilyGO boards much cheaper than traditional cellular modules ✅ Integrated Design: Built-in LTE modem eliminates external dongles ✅ Low Power: ESP32 consumes less power than Raspberry Pi solutions ✅ Real-Time: No OS overhead for critical flight operations ✅ Scalable: Easy to add multiple drones to same network infrastructure
SETUP…
Mount a LilyGO ESP32 board with integrated SIM card/LTE modem on a DJI F450 frame to build a drone independent of traditional RC links, operating with an IP-based (4G/5G) telemetry and control system. The aim is wide coverage and secure connectivity for long-range missions.
System Architecture
[Ground Station] —(Internet/VPN)— [Server (optional)] —(LTE)— [LilyGO ESP32] —(UART/MAVLink)— [Pixhawk/FC]
│ │
└— [Camera (optional)] └— [ESC/Motor]
│
└— [GPS/IMU/Sensors]
System Components:
- Flight Controller (FC): Pixhawk-compatible board (ArduPilot or PX4)
- Companion Computer: LilyGO T-SIM7000G or T-A7670G
- Connectivity: Integrated 4G/LTE modem + SIM card
- Ground Station: QGroundControl / Mission Planner (telemetry & mapping)
- Optional Server: Tunnel/VPN, MAVLink routing, logging
Bill of Materials (BOM)
Frame and Mechanical
- Frame: DJI F450 (original or clone) + vibration dampers
- Motors: 2212-2216, 800-1000 KV (×4) – e.g., DJI E305
- ESCs: 30A BLHeli_S/BLHeli_32 (×4) – SimonK firmware supported
- Propellers: 9×4.5 or 10×4.5 (2 CW + 2 CCW) – carbon fiber recommended
- Battery: 3S LiPo (3000-4000 mAh) or 4S (2200-3300 mAh), XT60 connector
- Power Distribution: Integrated PCB or separate PDB + UBEC (5V/3A, 12V/2A)
Electronics and Controller
- Flight Controller: Pixhawk 6C/6X, Cube Orange, or compatible clone
- GPS/Compass: Here3/Here4 RTK capable (recommended) or NEO-M8N minimum
- Telemetry: 915MHz/433MHz module (backup)
- RC Receiver: SBUS/PPM compatible (for failsafe)
Computing and Communication
- LilyGO Board:
- T-SIM7000G: ESP32 + SIM7000G (2G/3G/4G/NB-IoT)
- T-A7670G: ESP32-S3 + A7670G (4G LTE Cat-1)
- T-SIM7080G: ESP32-S3 + SIM7080G (4G LTE Cat-M/NB2)
- SIM Card: IoT data plan (static IP/VPN preferred)
- Antennas:
- LTE: 2×2 MIMO antenna (700-2700MHz)
- GPS: Active GPS antenna (if external GPS used)
- RC: 2.4GHz/915MHz antenna
Optional Components
- Camera: ESP32-CAM module or USB UVC camera
- Gimbal: 2-axis brushless gimbal
- FPV: Digital FPV system (DJI Air Unit, Walksnail etc.)
- Sensors: LiDAR (TFMini-S), optical flow sensor
Assembly and Protection
Hardware: M3/M2.5 screws, standoffs, zip ties
Enclosure: IP65 rated plastic case (for LilyGO and electronics)
Vibration Isolators: Gel dampers, anti-vibration pads
Cables: UART, USB, power cables – EMI shielded
Power System and Assembly
Power Distribution
Battery (11.1V/14.8V)
├── PDB → ESCs → Motors
├── UBEC (12V/2A) → Gimbal, Antennas
├── UBEC (5V/3A) → LilyGO ESP32, Camera
└── Linear Regulator → Pixhawk (5.5V)Software Stack
Flight Controller (Pixhawk)
# ArduPilot Copter firmware (recommended)
- ArduCopter 4.4+ (LTE telemetry support)
- Parameter configuration:
- SERIAL1_PROTOCOL = 2 (MAVLink2)
- SERIAL1_BAUD = 115200
- FS_THR_ENABLE = 1 (RC failsafe)
- RTL_ALT = 50 (RTL altitude 50m)
- FENCE_ENABLE = 1 (geofence active)LilyGO ESP32 Setup
// Arduino IDE setup for LilyGO boards
// Board: ESP32 Dev Module or ESP32S3 Dev Module
// Libraries needed:
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <HTTPClient.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
// LTE modem libraries (board specific)
#include <TinyGsmClient.h> // For SIM7000G/A7670G
// MAVLink library
#include <mavlink.h>Network Configuration
// LTE connection setup for LilyGO
void setupLTE() {
// Initialize modem
modem.restart();
modem.gprsConnect(apn, gprsUser, gprsPass);
// Check network registration
if (modem.isNetworkConnected()) {
Serial.println("Network connected");
}
}
// VPN connection (OpenVPN/WireGuard alternative for ESP32)
void setupSecureConnection() {
// Use HTTPS/WSS for secure communication
// Certificate-based authentication
}MAVLink Tunneling (over LTE)
LilyGO ESP32 Code
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
#include <WiFiClientSecure.h>
#include <ArduinoWebsockets.h>
// UART to Pixhawk
HardwareSerial pixhawkSerial(1);
WebsocketsClient wsClient;
void setup() {
// Initialize UART for Pixhawk communication
pixhawkSerial.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, 16, 17); // RX, TX pins
// Setup LTE connection
setupLTE();
// Connect to WebSocket server (secure tunnel)
wsClient.connect("wss://your-server.com/mavlink");
}
void loop() {
// Forward MAVLink from Pixhawk to server
if (pixhawkSerial.available()) {
String mavlinkData = pixhawkSerial.readString();
wsClient.send(mavlinkData);
}
// Forward commands from server to Pixhawk
if (wsClient.available()) {
String command = wsClient.readString();
pixhawkSerial.print(command);
}
}Simple UDP Bridge Alternative
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
WiFiUDP udp;
const char* serverIP = "your-vpn-server-ip";
const int serverPort = 14550;
void forwardMAVLink() {
// Read from Pixhawk UART
if (pixhawkSerial.available()) {
uint8_t buffer[512];
int len = pixhawkSerial.readBytes(buffer, sizeof(buffer));
// Send via UDP to ground station
udp.beginPacket(serverIP, serverPort);
udp.write(buffer, len);
udp.endPacket();
}
}